
Krypton (Kr)
| Atomic Number | 36 |
|---|---|
| Atomic Weight | 83.798 |
| Mass Number | 84 |
| Group | 18 |
|---|---|
| Period | 4 |
| Block | p |
| Protons | 36 p+ |
|---|---|
| Neutrons | 48 n0 |
| Electrons | 36 e- |
Physical Properties
| Atomic Radius | |
|---|---|
| Molar Volume | |
| Covalent Radius | |
| Metallic Radius | |
| Ionic Radius | |
| Crystal Radius | |
| Van der Waals Radius | |
| Density |
Chemical Properties
| Energy | |
|---|---|
| Proton Affinity | |
| Electron Affinity | |
| Ionization Energy | |
| Heat of Vaporization | |
| Heat of Fusion | |
| Heat of Formation | |
| Electrons | |
| Electron Shells | 2, 8, 18, 8 |
| Valence Electrons | 8 ⓘ |
| Electron Configuration | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p6ⓘ 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 |
| Oxidation States | 0, 1, 2 |
| Electronegativity | |
| Electrophilicity Index | |
| States of Matter | |
| Phase | {ERROR}|
| Gas Phase | Monoatomic |
| Boiling Point | |
| Melting Point | |
| Critical Pressure | |
| Critical Temperature | |
| Triple Point | |
| Visual | |
Krypton is a Black. Kr has a CPK of #ff1493, Jmol of #5cb8d1, and MOLCAS GV of #5cb8d1. The Appearance of Element 36 is colorless gas, exhibiting a whitish glow in a high electric field. The Refractive Index of Krypton (Kr) is 1.000427. | |
| Color | Black
|
| Appearance | colorless gas, exhibiting a whitish glow in a high electric field |
| Refractive Index | 1.000427
|
| Thermodynamic Properties | |
| Thermal Conductivity | |
| Thermal Expansion | |
| Molar Heat Capacity | |
| Specific Heat Capacity | |
| Heat Capacity Ratio (Adiabatic Index) | 5/3 |
| Electrical Properties | |
| Type | |
| Electrical Conductivity | |
| Electrical Resistivity | |
| Superconducting Point | |
| Magnetism | |
| Type | diamagnetic |
| Magnetic Susceptibility (Mass) | -0.0000000044 m³/Kg
|
| Magnetic Susceptibility (Molar) | -0.000000000369 m³/mol
|
| Magnetic Susceptibility (Volume) | -0.0000000165
|
| Magnetic Ordering | |
| Curie Point | |
| Neel Point | |
| Structure | |
The Crystal Structure of Krypton is FCC. The lattice constant of Kr is 5.72 Å. The lattice angles of Element 36 are π/2, π/2, π/2. | |
| Crystal Structure | {ERROR} |
| Lattice Constant | |
| Lattice Angles | π/2, π/2, π/2 |
| Mechanical Properties | |
The Speed of Sound of Krypton is 1120 m/s. | |
| Hardness | |
| Bulk Modulus | |
| Shear Modulus | |
| Young's Modulus | |
| Poisson Ratio | |
| Speed of Sound | |
| Classification | |
The CAS Group of Krypton is VIII. The IUPAC Group of Kr is VIIIA. The Glawe Number of Element 36 is 4. The Mendeleev Number of Krypton (Kr) is 115. The Pettifor Number of Krypton is 4. The Geochemical Class of Kr is volatile. The Goldschmidt Class of Element 36 is atmophile. | |
| Category | Actinides, Noble gases |
| CAS Group | VIII |
| IUPAC Group | VIIIA |
| Glawe Number | 4 |
| Mendeleev Number | 115 |
| Pettifor Number | 4 |
| Geochemical Class | volatile |
| Goldschmidt Class | atmophile |
Other
The Gas Basicity of Krypton is 402.4 kJ/mol. The Dipole Polarizability of Kr is 16.78 plus or minus 0.02 a₀. Element 36 has a C6 Dispersion Coefficient (CD) of 130 a₀, and C6 Dispersion Coefficient (GB) of 136 a₀. The Allotropes of Krypton (Kr) is . The Neutron Cross Section of Krypton is 25. The Neutron Mass Absorption of Kr is 0.013. The Quantum Numbers of Element 36 is 1S0. The Space Group of Krypton (Kr) is 225 (Fm_3m).
| Gas Basicity | |
|---|---|
| Dipole Polarizability | |
| C6 Dispersion Coefficient | |
| Allotropes | |
| Neutron Cross Section | 25
|
| Neutron Mass Absorption | 0.013
|
| Quantum Numbers | 1S0 |
| Space Group | 225 (Fm_3m) |
Isotopes of Krypton
| Stable Isotopes | 4 |
|---|---|
| Unstable Isotopes | 31 |
| Natural Isotopes | 6 |
67Kr
| Mass Number | 67 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 31 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | |
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 7.4 ± 2.9 ms
|
| Spin | 3/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | |
| Discovery Year | 2016 |
| Parity | - |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| 2p (2-proton emission) | 37% |
| β+ (β+ decay; β+ = ϵ + e+) |
68Kr
| Mass Number | 68 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 32 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 21.6 ± 3.3 ms
|
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 2016 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β+ (β+ decay; β+ = ϵ + e+) | |
| β+ p (β+-delayed proton emission) | 90% |
| p (proton emission) |
69Kr
| Mass Number | 69 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 33 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | |
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 27.9 ± 0.8 ms
|
| Spin | 5/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | |
| Discovery Year | 1995 |
| Parity | - |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β+ (β+ decay; β+ = ϵ + e+) | 100% |
| β+ p (β+-delayed proton emission) | 94% |
70Kr
| Mass Number | 70 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 34 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 45 ± 0.14 ms
|
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1995 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β+ (β+ decay; β+ = ϵ + e+) | 100% |
| β+ p (β+-delayed proton emission) | 1.3% |
71Kr
| Mass Number | 71 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 35 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | |
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 98.8 ± 0.3 ms
|
| Spin | 5/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | |
| Discovery Year | 1981 |
| Parity |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β+ (β+ decay; β+ = ϵ + e+) | 100% |
| β+ p (β+-delayed proton emission) | 2.1% |
72Kr
| Mass Number | 72 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 36 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 17.16 ± 0.18 s
|
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1973 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β+ (β+ decay; β+ = ϵ + e+) | 100% |
73Kr
| Mass Number | 73 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 37 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | |
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 27.3 ± 1 s
|
| Spin | 3/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | |
| Discovery Year | 1972 |
| Parity |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β+ (β+ decay; β+ = ϵ + e+) | 100% |
| β+ p (β+-delayed proton emission) | 0.25% |
74Kr
| Mass Number | 74 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 38 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 11.5 ± 0.11 m
|
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1960 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β+ (β+ decay; β+ = ϵ + e+) | 100% |
75Kr
| Mass Number | 75 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 39 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | -0.2124 ± 0.0016
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 4.6 ± 0.07 m
|
| Spin | 5/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 1.137 ± 0.013
|
| Discovery Year | 1960 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β+ (β+ decay; β+ = ϵ + e+) | 100% |
76Kr
| Mass Number | 76 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 40 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 14.8 ± 0.1 h
|
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1954 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β+ (β+ decay; β+ = ϵ + e+) | 100% |
77Kr
| Mass Number | 77 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 41 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | -0.2332 ± 0.0012
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 72.6 ± 0.9 m
|
| Spin | 5/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0.948 ± 0.01
|
| Discovery Year | 1948 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β+ (β+ decay; β+ = ϵ + e+) | 100% |
78Kr
| Mass Number | 78 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 42 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | 0.355 ± 0.003
|
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | |
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1920 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| 2β+ (double β+ decay) |
79Kr
| Mass Number | 79 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 43 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 1.072 ± 0.004
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 35.04 ± 0.1 h
|
| Spin | 1/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1948 |
| Parity | - |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β+ (β+ decay; β+ = ϵ + e+) | 100% |
80Kr
| Mass Number | 80 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 44 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | 2.286 ± 0.01
|
| Radioactivity | Stable |
| Half Life | Not Radioactive ☢️ |
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1920 |
| Parity | + |
81Kr
| Mass Number | 81 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 45 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | -0.25914285714286 ± 0.00057142857142857
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 229 ± 11 ky
|
| Spin | 7/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0.644 ± 0.004
|
| Discovery Year | 1950 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| ϵ (electron capture) | 100% |
82Kr
| Mass Number | 82 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 46 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | 11.593 ± 0.031
|
| Radioactivity | Stable |
| Half Life | Not Radioactive ☢️ |
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1920 |
| Parity | + |
83Kr
| Mass Number | 83 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 47 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | -0.21571777777778 ± 0.00000066666666666667
|
| Abundance | 11.5 ± 0.019
|
| Radioactivity | Stable |
| Half Life | Not Radioactive ☢️ |
| Spin | 9/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0.259 ± 0.001
|
| Discovery Year | 1920 |
| Parity | + |
84Kr
| Mass Number | 84 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 48 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | 56.987 ± 0.015
|
| Radioactivity | Stable |
| Half Life | Not Radioactive ☢️ |
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1920 |
| Parity | + |
85Kr
| Mass Number | 85 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 49 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | -0.22344444444444 ± 0.000088888888888889
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 10.728 ± 0.007 y
|
| Spin | 9/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0.443 ± 0.003
|
| Discovery Year | 1940 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
86Kr
| Mass Number | 86 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 50 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | 17.279 ± 0.041
|
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | |
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1920 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| 2β− (double β− decay) |
87Kr
| Mass Number | 87 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 51 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | -0.4088 ± 0.0008
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 76.3 ± 0.5 m
|
| Spin | 5/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | -0.3 ± 0.003
|
| Discovery Year | 1940 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
88Kr
| Mass Number | 88 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 52 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 2.825 ± 0.019 h
|
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1939 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
89Kr
| Mass Number | 89 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 53 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | -0.22 ± 0.002
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 3.15 ± 0.04 m
|
| Spin | 3/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0.166 ± 0.002
|
| Discovery Year | 1940 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
90Kr
| Mass Number | 90 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 54 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 32.32 ± 0.09 s
|
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1951 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
91Kr
| Mass Number | 91 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 55 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | -0.2332 ± 0.0008
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 8.57 ± 0.04 s
|
| Spin | 5/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0.303 ± 0.006
|
| Discovery Year | 1951 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
| β− n (β−-delayed neutron emission) |
92Kr
| Mass Number | 92 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 56 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 1.84 ± 0.008 s
|
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1951 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
| β− n (β−-delayed neutron emission) | 0.0332% |
93Kr
| Mass Number | 93 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 57 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | -0.826 ± 0.004
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 1.287 ± 0.01 s
|
| Spin | 1/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1951 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
| β− n (β−-delayed neutron emission) | 1.95% |
94Kr
| Mass Number | 94 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 58 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 212 ± 4 ms
|
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1972 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
| β− n (β−-delayed neutron emission) | 1.11% |
95Kr
| Mass Number | 95 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 59 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | -0.82 ± 0.006
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 114 ± 3 ms
|
| Spin | 1/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1994 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
| β− n (β−-delayed neutron emission) | 2.87% |
| 2n (2-neutron emission) |
96Kr
| Mass Number | 96 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 60 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 80 ± 8 ms
|
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1994 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
| β− n (β−-delayed neutron emission) | 3.7% |
97Kr
| Mass Number | 97 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 61 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | |
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 62.2 ± 3.2 ms
|
| Spin | 3/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | |
| Discovery Year | 1997 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
| β− n (β−-delayed neutron emission) | 6.7% |
| 2n (2-neutron emission) |
98Kr
| Mass Number | 98 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 62 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 42.8 ± 3.6 ms
|
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1997 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
| β− n (β−-delayed neutron emission) | 7% |
| 2n (2-neutron emission) |
99Kr
| Mass Number | 99 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 63 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | |
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 40 ± 11 ms
|
| Spin | 5/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | |
| Discovery Year | 1997 |
| Parity | - |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
| β− n (β−-delayed neutron emission) | 11% |
| 2n (2-neutron emission) |
100Kr
| Mass Number | 100 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 64 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 12 ± 8 ms
|
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1997 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
| β− n (β−-delayed neutron emission) | |
| 2n (2-neutron emission) |
101Kr
| Mass Number | 101 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 65 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | |
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | |
| Spin | 5/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | |
| Discovery Year | 2010 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | |
| β− n (β−-delayed neutron emission) | |
| 2n (2-neutron emission) |
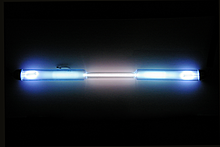
History
Scottish chemist Sir William Ramsay and his assistant English chemist Morris Travers discovered krypton in 1898 in London. They found krypton in the residue left from evaporating nearly all components of liquid air. William Ramsay was awarded the 1904 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for discovery of a series of noble gases, including krypton. From the Greek word kryptos, hidden
| Discoverers | Sir William Ramsey, M.W. Travers |
|---|---|
| Discovery Location | Great Britain |
| Discovery Year | 1898 |
| Etymology (Name Origin) | Greek: kryptos (hidden). |
| Pronunciation | KRIP-ton (English) |
Uses
Sources
Forms 1 millionth of the atmosphere. Obtained from production of liquid air.
| Abundance | |
|---|---|
| Abundance in Earth's crust | |
| Natural Abundance (Oceans) | |
| Natural Abundance (Human Body) | |
| Natural Abundance (Meteor) | |
| Natural Abundance (Sun) | |
| Abundance in Universe | 0.000004 %
|
Nuclear Screening Constants
| 1 | s | 0.7684 |
| 2 | p | 3.953 |
| 2 | s | 9.602 |
| 3 | d | 15.3741 |
| 3 | p | 15.5658 |
| 3 | s | 14.9673 |
| 4 | p | 26.2308 |
| 4 | s | 24.6844 |
Also Known As
- Kr
- element 36
- 36Kr
Translations
- Norwegian Bokmålkrypton
- Frenchkrypton
- Italiankripton
- Russianкриптон
- GermanKrypton
- Dutchkrypton
- Spanishkriptón
- Danishkrypton
- Norwegian Nynorskkrypton
- Hungariankripton
- Polishkrypton
- Afrikaanskripton
- Amharicክሪፕተን
- AragoneseCriptón
- Arabicكريبتون
- AzerbaijaniKripton
- BelarusianКрыптон
- Bulgarianкриптон
- Banglaক্রিপ্টন
- BretonKripton
- Bosniankripton
- Catalancriptó
- CorsicanKriptone
- Czechkrypton
- ChuvashКриптон
- WelshCrypton
- Greekκρυπτό
- Esperantokriptono
- Estoniankrüptoon
- Basquekripton
- Persianکریپتون
- Finnishkrypton
- FriulianCripton
- Western FrisianKrypton
- IrishCrioptón
- Galiciancripton
- ManxKrypton
- Hakka ChineseKrypton
- Hebrewקריפטון
- Hindiक्रिप्टन
- Fiji HindiKrypton
- CroatianKripton
- Haitian CreoleKripton
- Armenianկրիպտոն
- Interlinguakrypton
- Indonesiankripton
- Idokriptono
- Icelandickrypton
- Japaneseクリプトン
- Lojbanmipnavni
- JavaneseKripton
- Georgianკრიპტონი
- KazakhКриптон
- Kannadaಕ್ರಿಪ್ಟಾನ್
- Korean크립톤
- KomiКриптон
- Latinkrypton
- LuxembourgishKrypton
- LimburgishKrypton
- LigurianKripton
- LithuanianKriptonas
- Latviankriptons
- MacedonianКриптон
- Malayalamക്രിപ്റ്റോൺ
- Marathiक्रिप्टॉन
- Western MariКриптон
- MalayKripton
- Low GermanKrypton
- OccitanCripton
- Punjabiਕ੍ਰਿਪਟਨ
- Western Panjabiکرپٹون
- Portuguesecrípton
- QuechuaKriptun
- Romaniankripton
- Siciliancripton
- Serbo-CroatianKripton
- SlovakKryptón
- SlovenianKripton
- Serbianкриптон
- Saterland FrisianKrypton
- Swedishkrypton
- SwahiliKriptoni
- Tamilகிருப்டான்
- Thaiคริปทอน
- TagalogKriptono
- TurkishKripton
- Uyghurكرىپتون
- Ukrainianкриптон
- UzbekKripton
- VepsKripton
- Vietnamesekrypton
- WarayKripton
- KalmykКриптон
- Yiddishקריפטאן
- YorubaKrypton
- Chinese氪
- CebuanoKripton
- Central Kurdishکریپتۆن
- Northern FrisianKrypton
- Odiaକ୍ରିପ୍ଟନ
- Gujaratiક્રિપ્ટોન
- TatarКриптон
- PiedmonteseKrìpton
- Scotskrypton
- SomaliKiribtoon
- ErzyaКриптон
- Literary Chinese氪
- Cantonese氪
- Belarusian (Taraskievica orthography)крыптон
- English (United Kingdom)krypton
- Newariक्रिप्टन
- AlbanianKriptoni
- AromanianKripton
- Church SlavicКрѷптонъ
- FaroeseKrypton
- KyrgyzКриптон
- cdoKáik
- Burmeseကရစ်ပတွန်
- Nepaliक्रिप्टन
- Maltesekripton
- AsturianCriptón
- LombardKripton
- Scottish GaelicCriopton
- Portuguese (Brazil)criptônio
- Gan Chinese氪
- Sanskritक्रिप्टान
- Bhojpuriक्रिप्टन
- Min Nan ChineseKrypton
- SinhalaKripton
- Mongolianкриптон
- Tibetanསྦས་རླུང་།
- SundaneseKripton
- Mapuchekripton
- Lingua Franca Novacripton
- kbpKrɩpɩtɔnɩ
- Teluguక్రిప్టాన్
- Wu Chinese氪
- oloKriptounu
- Chinese (Traditional)氪
- Chinese (Taiwan)氪
- TajikКриптон
- Chinese (Simplified)氪
- SardinianCriptòn
- azbکریپتون
- BashkirКриптон
- Moroccan Arabicكريپتون
- German (Switzerland)Krypton
- English (Canada)Krypton
- Egyptian Arabicكريبتون
- Pashtoکرېپټون
- BikolKrypton
- CornishKrypton
- BalineseKripton
- Chinese (Hong Kong SAR China)氪
- Urduکرپٹون
- GandaKeriputooni
- Northern Samikrypton
- Inari Samikrypton
- ZuluUmKhalahwe




