
Oxygen (O)
| Atomic Number | 8 |
|---|---|
| Atomic Weight | 15.999 |
| Mass Number | 16 |
| Group | 16 |
|---|---|
| Period | 2 |
| Block | p |
| Protons | 8 p+ |
|---|---|
| Neutrons | 8 n0 |
| Electrons | 8 e- |
Physical Properties
| Atomic Radius | |
|---|---|
| Molar Volume | |
| Covalent Radius | |
| Metallic Radius | |
| Ionic Radius | |
| Crystal Radius | |
| Van der Waals Radius | |
| Density |
Chemical Properties
| Energy | |
|---|---|
| Proton Affinity | |
| Electron Affinity | |
| Ionization Energy | |
| Heat of Vaporization | |
| Heat of Fusion | |
| Heat of Formation | |
| Electrons | |
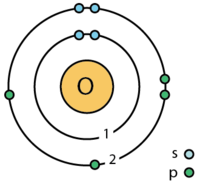
| Electron Shells | 2, 6 |
| Valence Electrons | 6 ⓘ |
| Electron Configuration | [He] 2s2 2p4ⓘ 1s2 2s2 2p4 |
| Oxidation States | -2, -1, 0, 1, 2 |
| Electronegativity |
3.44
|
| Electrophilicity Index | |
| States of Matter | |
| Phase | {ERROR}|
| Gas Phase | Diatomic |
| Boiling Point | |
| Melting Point | |
| Critical Pressure | |
| Critical Temperature | |
| Triple Point | |
| Visual | |
Oxygen is a Black. O has a CPK of #f00000, Jmol of #ff0d0d, and MOLCAS GV of #f32e42. The Refractive Index of Element 8 is 1.000271. | |
| Color | Black
|
| Appearance | |
| Refractive Index | 1.000271
|
| Thermodynamic Properties | |
| Thermal Conductivity | |
| Thermal Expansion | |
| Molar Heat Capacity | |
| Specific Heat Capacity | |
| Heat Capacity Ratio (Adiabatic Index) | 7/5 |
| Electrical Properties | |
| Type | |
| Electrical Conductivity | |
| Electrical Resistivity | |
| Superconducting Point | |
| Magnetism | |
| Type | paramagnetic |
| Magnetic Susceptibility (Mass) | 0.000001335 m³/Kg
|
| Magnetic Susceptibility (Molar) | 0.0000000427184 m³/mol
|
| Magnetic Susceptibility (Volume) | 0.00000190772
|
| Magnetic Ordering | |
| Curie Point | |
| Neel Point | |
| Structure | |
The Crystal Structure of Oxygen is CUB. The lattice constant of O is 6.83 Å. The lattice angles of Element 8 are π/2, 2.313085, π/2. | |
| Crystal Structure | {ERROR} |
| Lattice Constant | |
| Lattice Angles | π/2, 2.313085, π/2 |
| Mechanical Properties | |
The Speed of Sound of Oxygen is 317.5 m/s. | |
| Hardness | |
| Bulk Modulus | |
| Shear Modulus | |
| Young's Modulus | |
| Poisson Ratio | |
| Speed of Sound | |
| Classification | |
The CAS Group of Oxygen is VIB. The IUPAC Group of O is VIA. The Glawe Number of Element 8 is 97. The Mendeleev Number of Oxygen (O) is 99. The Pettifor Number of Oxygen is 101. The Geochemical Class of O is major. The Goldschmidt Class of Element 8 is litophile. | |
| Category | Actinides, Nonmetals |
| CAS Group | VIB |
| IUPAC Group | VIA |
| Glawe Number | 97 |
| Mendeleev Number | 99 |
| Pettifor Number | 101 |
| Geochemical Class | major |
| Goldschmidt Class | litophile |
Other
The Gas Basicity of Oxygen is 459.6 kJ/mol. The Dipole Polarizability of O is 5.3 plus or minus 0.2 a₀. Element 8 has a C6 Dispersion Coefficient (CD) of 15.6 a₀, and C6 Dispersion Coefficient (GB) of 16.7 a₀. The Allotropes of Oxygen (O) are Dioxygen, Ozone, Tetraoxygen. The Neutron Cross Section of Oxygen is 0.00028. The Neutron Mass Absorption of O is 1.0E-6. The Quantum Numbers of Element 8 is 3P2. The Space Group of Oxygen (O) is 12 (C12/m1).
| Gas Basicity | |
|---|---|
| Dipole Polarizability | |
| C6 Dispersion Coefficient | |
| Allotropes | Dioxygen, Ozone, Tetraoxygen |
| Neutron Cross Section | 0.00028
|
| Neutron Mass Absorption | 0.000001
|
| Quantum Numbers | 3P2 |
| Space Group | 12 (C12/m1) |
Isotopes of Oxygen
| Stable Isotopes | 3 |
|---|---|
| Unstable Isotopes | 15 |
| Natural Isotopes | 3 |
11O
| Mass Number | 11 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 3 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | |
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 198 ± 12 ys
|
| Spin | 3/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | |
| Discovery Year | 2019 |
| Parity | - |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| 2p (2-proton emission) | 100% |
12O
| Mass Number | 12 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 4 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 8.9 ± 3.3 zs
|
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1978 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| 2p (2-proton emission) | 100% |
13O
| Mass Number | 13 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 5 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0.92613333333333 ± 0.0002
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 8.58 ± 0.05 ms
|
| Spin | 3/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0.0111 ± 0.0008
|
| Discovery Year | 1963 |
| Parity | - |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β+ (β+ decay; β+ = ϵ + e+) | 100% |
| β+ p (β+-delayed proton emission) | 10.9% |
14O
| Mass Number | 14 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 6 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 70.621 ± 0.011 s
|
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1949 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β+ (β+ decay; β+ = ϵ + e+) | 100% |
15O
| Mass Number | 15 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 7 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 1.43816 ± 0.00024
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 122.266 ± 0.043 s
|
| Spin | 1/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1934 |
| Parity | - |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β+ (β+ decay; β+ = ϵ + e+) | 100% |
16O
| Mass Number | 16 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 8 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | 99.757 ± 0.011
|
| Radioactivity | Stable |
| Half Life | Not Radioactive ☢️ |
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1919 |
| Parity | + |
17O
| Mass Number | 17 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 9 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | -0.7574172 ± 0.000004
|
| Abundance | 0.03835 ± 0.00096
|
| Radioactivity | Stable |
| Half Life | Not Radioactive ☢️ |
| Spin | 5/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | |
| Discovery Year | 1925 |
| Parity | + |
18O
| Mass Number | 18 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 10 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | 0.2045 ± 0.0102
|
| Radioactivity | Stable |
| Half Life | Not Radioactive ☢️ |
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1929 |
| Parity | + |
19O
| Mass Number | 19 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 11 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0.612952 ± 0.000028
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 26.47 ± 0.006 s
|
| Spin | 5/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0.00362 ± 0.00013
|
| Discovery Year | 1936 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
20O
| Mass Number | 20 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 12 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 13.51 ± 0.05 s
|
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1959 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
21O
| Mass Number | 21 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 13 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | |
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 3.42 ± 0.1 s
|
| Spin | 5/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | |
| Discovery Year | 1968 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
| β− n (β−-delayed neutron emission) |
22O
| Mass Number | 22 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 14 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 2.25 ± 0.09 s
|
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1969 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
| β− n (β−-delayed neutron emission) | 22% |
23O
| Mass Number | 23 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 15 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | |
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 97 ± 8 ms
|
| Spin | 1/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1970 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
| β− n (β−-delayed neutron emission) | 7% |
24O
| Mass Number | 24 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 16 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 77.4 ± 4.5 ms
|
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 1970 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
| β− n (β−-delayed neutron emission) | 43% |
25O
| Mass Number | 25 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 17 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | |
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 5.18 ± 0.35 zs
|
| Spin | 3/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | |
| Discovery Year | 2008 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| n (neutron emission) | 100% |
26O
| Mass Number | 26 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 18 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | 4.2 ± 3.3 ps
|
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | 2012 |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| 2n (2-neutron emission) | 100% |
27O
| Mass Number | 27 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 19 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | |
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | |
| Spin | 3/2 |
| Quadrupole Moment | |
| Discovery Year | |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| n (neutron emission) | |
| 2n (2-neutron emission) |
28O
| Mass Number | 28 |
|---|---|
| Neutron Number | 20 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| G-Factor | 0
|
| Abundance | |
| Radioactivity | ☢️ Radioactive |
| Half Life | |
| Spin | 0 |
| Quadrupole Moment | 0
|
| Discovery Year | |
| Parity | + |
| Decay Mode | Intensity |
|---|---|
| 2n (2-neutron emission) | |
| β− (β− decay) | 0% |

History
Carl Wilhelm Scheele obtained oxygen by heating mercuric oxide and nitrates in 1771, but did not publish his findings until 1777. Joseph Priestley also prepared this new air by 1774. The name oxygen was coined in 1777 by Antoine Lavoisier, whose experiments with oxygen helped to discredit the then-popular phlogiston theory of combustion and corrosion. From the Greek word oxys, acid, and genes, forming
| Discoverers | Joseph Priestly, Carl Wilhelm Scheele |
|---|---|
| Discovery Location | England/Sweden |
| Discovery Year | 1774 |
| Etymology (Name Origin) | Greek: oxys and genes, (acid former). |
| Pronunciation | OK-si-jen (English) |
Uses
Sources
Obtained primarily from liquid air by fractional distillation. Small amounts are made in the laboratory by electrolysis of water or heating potassium chlorate (KClO3) with manganese dioxide (MnO2) catalyst.
| Abundance | |
|---|---|
| Abundance in Earth's crust | |
| Natural Abundance (Oceans) | |
| Natural Abundance (Human Body) | 61 %
|
| Natural Abundance (Meteor) | 40 %
|
| Natural Abundance (Sun) | 0.9 %
|
| Abundance in Universe | 1 %
|
Nuclear Screening Constants
| 1 | s | 0.3421 |
| 2 | p | 3.5468 |
| 2 | s | 3.5084 |
Also Known As
- O
- element 8
- 8O
- oxygen atom
Translations
- Frenchoxygène
- Polishtlen
- Italianossigeno
- Norwegian Bokmåloksygen
- Russianкислород
- GermanSauerstoff
- Spanishoxígeno
- Dutchzuurstof
- Ilokooksiheno
- Chinese (Traditional)氧
- Upper SorbianKislik
- Esperantooksigeno
- Hebrewחמצן
- Afrikaanssuurstof
- Amharicኦክሲጅን
- AragoneseOxichén
- Old EnglishÆðmlyft
- Arabicأكسجين
- Egyptian Arabicاوكسيجين
- Assameseঅক্সিজেন
- AsturianOxíxenu
- Azerbaijanioksigen
- BashkirКислород
- BavarianSauastoff
- Belarusianкісларод
- Bulgarianкислород
- Banglaঅক্সিজেন
- Tibetanགསོ་རླུང་།
- BretonOksigen
- Bosniankisik
- Catalanoxigen
- Central Kurdishئۆکسجین
- CorsicanOssigenu
- Czechkyslík
- ChuvashЙӳçлĕк
- Welshocsigen
- Danishilt
- Greekοξυγόνο
- Estonianhapnik
- Basqueoxigeno
- Persianاکسیژن
- Finnishhappi
- Northern FrisianSürstoof
- FriulianOssigjen
- Western Frisiansoerstof
- IrishOcsaigin
- Scottish GaelicOgsaidean
- Galicianosíxeno
- GuaraniTatarapo
- Gujaratiપ્રાણવાયુ
- Manxocsygien
- Hakka ChineseYòng
- Hawaiian‘Okikene
- Hindiऑक्सीजन
- Fiji HindiOxygen
- CroatianKisik
- Haitian CreoleOksijèn
- Hungarianoxigén
- Armenianթթվածին
- Interlinguaoxygeno
- Indonesianoksigen
- Idooxo
- Icelandicsúrefni
- Japanese酸素
- Lojbankijno
- JavaneseOksigèn
- Georgianჟანგბადი
- KazakhОттегі
- Kannadaಆಮ್ಲಜನಕ
- Korean산소
- Komi-PermyakШӧмувтыр
- ColognianSauerstoff
- KurdishOksîjen
- KomiШомвачужысь
- Latinoxygenium
- LuxembourgishSauerstoff
- LimburgishZuurstof
- LigurianOscigeno
- LombardUssigen
- LingalaOksijɛ́ní
- Lithuaniandeguonis
- Latvianskābeklis
- MokshaШапафни
- MalagasyÔksizenina
- Mariшопештыш
- Māorihāora
- Macedonianкислород
- Malayalamഓക്സിജൻ
- Mongolianхүчилтөрөгч
- Marathiऑक्सिजन
- Western MariКислород
- Malayoksigen
- Malteseossiġenu
- Burmeseအောက်စီဂျင်
- ErzyaЧапамо чачтый
- nahEhēcayoh
- Low GermanSuerstoff
- Nepaliअक्सिजन
- Newariअक्सिजन
- Norwegian Nynorskoksygen
- NavajoNíłchʼi Yáʼátʼéehii
- Occitanoxigèn
- OromoOxygen
- OsseticТуаггуыр
- Punjabiਆਕਸੀਜਨ
- PampangaOxygen
- Papiamentooksígeno
- Western Panjabiآکسیجن
- Pashtoآکسيجن
- Portugueseoxigénio
- QuechuaMuksichaq
- Romanianoxigen
- RusynОксід
- Sicilianossìgginu
- Serbo-CroatianKiseonik
- Sinhalaඔක්සිජන්
- Slovakkyslík
- Sloveniankisik
- Somalioxygen
- Albanianoksigjeni
- Serbianкисеоник
- Saterland FrisianSuurstof
- Sundaneseoksigén
- Swedishsyre
- SwahiliOksijeni
- Tamilஒட்சிசன்
- Teluguఆక్సిజన్
- Tajikоксиген
- Thaiออกซิเจน
- TagalogOksiheno
- Turkishoksijen
- Tatarуттуар
- Uyghurئوكسىگېن
- UkrainianОксиген
- Urduآکسیجن
- UzbekKislorod
- Venetianosìxeno
- Vepshapanik
- Vietnameseoxy
- WarayOksiheno
- KalmykКүчлтөр
- Yiddishזויערשטאף
- YorubaỌ́ksíjìn
- ZhuangYangj
- Chinese氧
- German (Switzerland)Sauerstoff
- English (Canada)Oxygen
- English (United Kingdom)oxygen
- Portuguese (Brazil)oxigênio
- CebuanoOksihena
- Scotsoxygen
- Odiaଅମ୍ଳଜାନ
- KikuyuOxygen
- Cantonese氧
- Chinese (China)氧
- Chinese (Hong Kong SAR China)氧
- Swiss GermanSuurstoff
- SamogitianDegounis
- Min Nan ChineseSng-sò͘
- Literary Chinese氧
- Belarusian (Taraskievica orthography)тлен
- Chinese (Simplified)氧
- Laoອົກຊີແຊນ
- BuriatХүшэлтүрэгшэ
- PiedmonteseOssìgen
- WalloonOcsidjinne
- YakutКислород
- West FlemishZuurstof
- LezghianКислород
- AromanianOxigenu
- RomanshOxigen
- cdoIōng
- FaroeseSúrevni
- SardinianOssìgenu
- KyrgyzКычкылтек
- Goan Konkaniऑक्सिजन
- Gan Chinese氧
- Bhojpuriऑक्सीजन
- azbاوکسیژن
- Sindhiآڪسيجن
- Volapükloxin
- XhosaI-oxygen
- Jamaican Creole EnglishAxijen
- oloHappamehsuadu
- Chinese (Macao SAR China)氧
- Chinese (Malaysia)氧
- Chinese (Singapore)氧
- Chinese (Taiwan)氧
- Goan Konkani (Latin)Oxygen
- Goan Konkani (Devanagari)ऑक्सिजन
- Paliअक्सिजन
- Lingua Franca Novaosijen
- Tatar (Cyrillic)уттуар
- Wu Chinese氧
- CherokeeᎤᏬᎳᏕᏍᏗ
- ChechenМустлург
- Khmerអុកស៊ីសែន
- Mingrelianჟანგბადი
- Tuluಆಮ್ಲಜನಕ
- kbpƆkɩsɩzɛnɩ
- ExtremaduranOssígenu
- KabyleUksijin
- hywԹթուածին
- gcrOksijèn
- Skolt Samihapp
- Moroccan Arabicأوكسيجين
- FijianOkosijeni
- BalineseOksigén
- Cornishoksyjen
- lldOssigen
- BikolOksiheno
- Manipuriꯑꯣꯛꯁꯤꯖꯦꯟ
- Inari Samihappi
- MinangkabauOksigen
- Northern Samioksygena
- Crimean Tataroksigen
- Zuluumoya-mpilo
- Malay (Arabic)اوکسيݢن
- Kashmiriآکسیجَن
- Hausaiskar shaƙa
- skrآکسیجن
- blkအောက်သီစဲန်
- Lower Sorbiankislik
- Silesiantlyn




