
Oksijɛ́ní (O)
chemical element, symbol O and atomic number 8
| Atomic Number | 8 |
|---|---|
| Atomic Weight | 15.999 |
| mass number | 16 |
| Group | 16 |
|---|---|
| Period | 2 |
| Block | p |
| Proton | 8 p+ |
|---|---|
| Netron | 8 n0 |
| Eléktron | 8 e- |
Physical Property
| Atomic Radius | |
|---|---|
| molar volume | |
| covalent radius | |
| Metallic Radius | |
| ionic radius | |
| Crystal Radius | |
| Van der Waals radius | |
| density |
Chemical Property
| molungé | |
|---|---|
| proton affinity | |
| electron affinity | |
| ionization energy | |
| enthalpy of vaporization | |
| enthalpy of fusion | |
| standard enthalpy of formation | |
| Eléktron | |
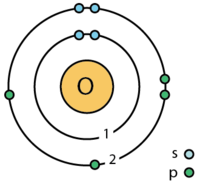
| electron shell | 2, 6 |
| valence electron | 6 ⓘ |
| electron configuration | [He] 2s2 2p4ⓘ 1s2 2s2 2p4 |
| oxidation number | -2, -1, 0, 1, 2 |
| electronegativity |
3.44
|
| Electrophilicity Index | |
| fundamental state of matter | |
| phase of matter | {ERROR}|
| gaseous state of matter | Diatomic |
| Boiling Point | |
| Melting Point | |
| critical pressure | |
| critical temperature | |
| triple point | |
| appearance | |
| Lángi | Black
|
| appearance | |
| refractive index | 1,000271
|
| thermodynamic material property | |
| Thermal Conductivity | |
| thermal expansion | |
| molar heat capacity | |
| Specific Heat Capacity | |
| heat capacity ratio | 7/5 |
| electrical properties | |
| type | |
| electrical conductivity | |
| electrical resistivity | |
| superconductivity | |
| magnetism | |
| type | paramagnetic |
| magnetic susceptibility (Mass) | 0,000001335 m³/Kg
|
| magnetic susceptibility (Molar) | 0,0000000427184 m³/mol
|
| magnetic susceptibility (Volume) | 0,00000190772
|
| magnetic ordering | |
| Curie temperature | |
| Néel temperature | |
| structure | |
| Crystal Structure | {ERROR} |
| lattice constant | |
| Lattice Angles | π/2, 2.313085, π/2 |
| mechanical property | |
| hardness | |
| bulk modulus | |
| shear modulus | |
| Young's modulus | |
| Poisson's ratio | |
| speed of sound | |
| classification | |
| Category | Actinides, Nonmetals |
| CAS Group | VIB |
| IUPAC Group | VIA |
| Glawe Number | 97 |
| Mendeleev Number | 99 |
| Pettifor Number | 101 |
| Geochemical Class | major |
| Goldschmidt classification | litophile |
other
| Gas Basicity | |
|---|---|
| polarizability | |
| C6 Dispersion Coefficient | |
| allotrope | Dioxygen, Ozone, Tetraoxygen |
| Neutron cross section | 0,00028
|
| Neutron Mass Absorption | 0,000001
|
| quantum number | 3P2 |
| space group | 12 (C12/m1) |
Isotopes of Oxygen
| Stable Isotopes | 3 |
|---|---|
| Unstable Isotopes | 15 |
| Natural Isotopes | 3 |
11O
| mass number | 11 |
|---|---|
| neutron number | 3 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| g-factor | |
| natural abundance | |
| radioactivity | ☢️ radioactive element |
| half-life | 198 ± 12 ys
|
| spin | 3/2 |
| nuclear quadrupole moment | |
| time of discovery or invention | 2019 |
| parity | - |
| decay mode | intensity |
|---|---|
| 2p (2-proton emission) | 100% |
12O
| mass number | 12 |
|---|---|
| neutron number | 4 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| g-factor | 0
|
| natural abundance | |
| radioactivity | ☢️ radioactive element |
| half-life | 8,9 ± 3,3 zs
|
| spin | 0 |
| nuclear quadrupole moment | 0
|
| time of discovery or invention | 1978 |
| parity | + |
| decay mode | intensity |
|---|---|
| 2p (2-proton emission) | 100% |
13O
| mass number | 13 |
|---|---|
| neutron number | 5 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| g-factor | 0,92613333333333 ± 0,0002
|
| natural abundance | |
| radioactivity | ☢️ radioactive element |
| half-life | 8,58 ± 0,05 ms
|
| spin | 3/2 |
| nuclear quadrupole moment | 0,0111 ± 0,0008
|
| time of discovery or invention | 1963 |
| parity | - |
| decay mode | intensity |
|---|---|
| β+ (β+ decay; β+ = ϵ + e+) | 100% |
| β+ p (β+-delayed proton emission) | 10.9% |
14O
| mass number | 14 |
|---|---|
| neutron number | 6 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| g-factor | 0
|
| natural abundance | |
| radioactivity | ☢️ radioactive element |
| half-life | 70,621 ± 0,011 s
|
| spin | 0 |
| nuclear quadrupole moment | 0
|
| time of discovery or invention | 1949 |
| parity | + |
| decay mode | intensity |
|---|---|
| β+ (β+ decay; β+ = ϵ + e+) | 100% |
15O
| mass number | 15 |
|---|---|
| neutron number | 7 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| g-factor | 1,43816 ± 0,00024
|
| natural abundance | |
| radioactivity | ☢️ radioactive element |
| half-life | 122,266 ± 0,043 s
|
| spin | 1/2 |
| nuclear quadrupole moment | 0
|
| time of discovery or invention | 1934 |
| parity | - |
| decay mode | intensity |
|---|---|
| β+ (β+ decay; β+ = ϵ + e+) | 100% |
16O
| mass number | 16 |
|---|---|
| neutron number | 8 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| g-factor | 0
|
| natural abundance | 99,757 ± 0,011
|
| radioactivity | stable isotope |
| half-life | Not Radioactive ☢️ |
| spin | 0 |
| nuclear quadrupole moment | 0
|
| time of discovery or invention | 1919 |
| parity | + |
17O
| mass number | 17 |
|---|---|
| neutron number | 9 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| g-factor | -0,7574172 ± 0,000004
|
| natural abundance | 0,03835 ± 0,00096
|
| radioactivity | stable isotope |
| half-life | Not Radioactive ☢️ |
| spin | 5/2 |
| nuclear quadrupole moment | |
| time of discovery or invention | 1925 |
| parity | + |
18O
| mass number | 18 |
|---|---|
| neutron number | 10 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| g-factor | 0
|
| natural abundance | 0,2045 ± 0,0102
|
| radioactivity | stable isotope |
| half-life | Not Radioactive ☢️ |
| spin | 0 |
| nuclear quadrupole moment | 0
|
| time of discovery or invention | 1929 |
| parity | + |
19O
| mass number | 19 |
|---|---|
| neutron number | 11 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| g-factor | 0,612952 ± 0,000028
|
| natural abundance | |
| radioactivity | ☢️ radioactive element |
| half-life | 26,47 ± 0,006 s
|
| spin | 5/2 |
| nuclear quadrupole moment | 0,00362 ± 0,00013
|
| time of discovery or invention | 1936 |
| parity | + |
| decay mode | intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
20O
| mass number | 20 |
|---|---|
| neutron number | 12 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| g-factor | 0
|
| natural abundance | |
| radioactivity | ☢️ radioactive element |
| half-life | 13,51 ± 0,05 s
|
| spin | 0 |
| nuclear quadrupole moment | 0
|
| time of discovery or invention | 1959 |
| parity | + |
| decay mode | intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
21O
| mass number | 21 |
|---|---|
| neutron number | 13 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| g-factor | |
| natural abundance | |
| radioactivity | ☢️ radioactive element |
| half-life | 3,42 ± 0,1 s
|
| spin | 5/2 |
| nuclear quadrupole moment | |
| time of discovery or invention | 1968 |
| parity | + |
| decay mode | intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
| β− n (β−-delayed neutron emission) |
22O
| mass number | 22 |
|---|---|
| neutron number | 14 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| g-factor | 0
|
| natural abundance | |
| radioactivity | ☢️ radioactive element |
| half-life | 2,25 ± 0,09 s
|
| spin | 0 |
| nuclear quadrupole moment | 0
|
| time of discovery or invention | 1969 |
| parity | + |
| decay mode | intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
| β− n (β−-delayed neutron emission) | 22% |
23O
| mass number | 23 |
|---|---|
| neutron number | 15 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| g-factor | |
| natural abundance | |
| radioactivity | ☢️ radioactive element |
| half-life | 97 ± 8 ms
|
| spin | 1/2 |
| nuclear quadrupole moment | 0
|
| time of discovery or invention | 1970 |
| parity | + |
| decay mode | intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
| β− n (β−-delayed neutron emission) | 7% |
24O
| mass number | 24 |
|---|---|
| neutron number | 16 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| g-factor | 0
|
| natural abundance | |
| radioactivity | ☢️ radioactive element |
| half-life | 77,4 ± 4,5 ms
|
| spin | 0 |
| nuclear quadrupole moment | 0
|
| time of discovery or invention | 1970 |
| parity | + |
| decay mode | intensity |
|---|---|
| β− (β− decay) | 100% |
| β− n (β−-delayed neutron emission) | 43% |
25O
| mass number | 25 |
|---|---|
| neutron number | 17 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| g-factor | |
| natural abundance | |
| radioactivity | ☢️ radioactive element |
| half-life | 5,18 ± 0,35 zs
|
| spin | 3/2 |
| nuclear quadrupole moment | |
| time of discovery or invention | 2008 |
| parity | + |
| decay mode | intensity |
|---|---|
| n (neutron emission) | 100% |
26O
| mass number | 26 |
|---|---|
| neutron number | 18 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| g-factor | 0
|
| natural abundance | |
| radioactivity | ☢️ radioactive element |
| half-life | 4,2 ± 3,3 ps
|
| spin | 0 |
| nuclear quadrupole moment | 0
|
| time of discovery or invention | 2012 |
| parity | + |
| decay mode | intensity |
|---|---|
| 2n (2-neutron emission) | 100% |
27O
| mass number | 27 |
|---|---|
| neutron number | 19 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| g-factor | |
| natural abundance | |
| radioactivity | ☢️ radioactive element |
| half-life | |
| spin | 3/2 |
| nuclear quadrupole moment | |
| time of discovery or invention | |
| parity | + |
| decay mode | intensity |
|---|---|
| n (neutron emission) | |
| 2n (2-neutron emission) |
28O
| mass number | 28 |
|---|---|
| neutron number | 20 |
| Relative Atomic Mass | |
| g-factor | 0
|
| natural abundance | |
| radioactivity | ☢️ radioactive element |
| half-life | |
| spin | 0 |
| nuclear quadrupole moment | 0
|
| time of discovery or invention | |
| parity | + |
| decay mode | intensity |
|---|---|
| 2n (2-neutron emission) | |
| β− (β− decay) | 0% |

lisoló
| discoverer or inventor | Joseph Priestly, Carl Wilhelm Scheele |
|---|---|
| location of discovery | England/Sweden |
| time of discovery or invention | 1774 |
| etymology | Greek: oxys and genes, (acid former). |
| pronunciation | OK-si-jen (lingɛlɛ́sa) |
source
| Abundance | |
|---|---|
| Abundance in Earth's crust | |
| natural abundance (ocean) | |
| natural abundance (human body) | 61 %
|
| natural abundance (meteoroid) | 40 %
|
| natural abundance (Mói) | 0,9 %
|
| Abundance in Universe | 1 %
|
Nuclear Screening Constants
| 1 | s | 0.3421 |
| 2 | p | 3.5468 |
| 2 | s | 3.5084 |




